Video Article Open Access
Super-Resolution: An Adventure on A New Dimension
Peng Xi1,2
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, College of Future Technology, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
2 National Biomedical Imaging Center, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
Vid. Proc. Adv. Mater., Volume 3, Article ID 2210374 (2022)
DOI: 10.5185/vpoam.2022.10374
Publication Date (Web): 27 Nov 2023
Copyright © IAAM
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
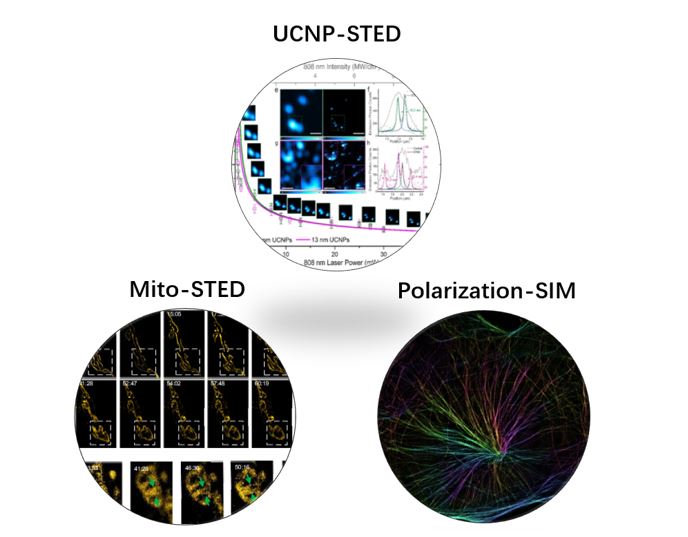
Super-resolution microscopy (SRM) breaks the diffraction limit of conventional optical microscopy, to reach spatial resolution <200 nm. Of the SRM, stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy employs a donut-beam confined excitation to project an optically saturated virtual pinhole for super-resolution. STED microscopy often obeys a “square-root law” for resolution and STED laser power, which means the power increases quadratically for better resolution. This approach is practically limited by the fragileness of the biological subcellular structure and the fluorescent dye. Here we present several novel techniques:
- Upconversion enabled ultralow power STED: Owing to the rich energy levels, we can create unique “route” for upconversion process, thus ultralow power STED can be realized.
- With novel mitochondria inner membrane dyes, we visualized the cristae remodelling, fusion and fission processes with long-term STED super-resolution.
- We developed fluorescence dipole orientation super-resolution microscopy and demonstrate that the polarization information provides a new dimension for super-resolution.
Keywords
Stimulated emission depletion, structured illumination microscopy, polarization, up conversion.
Acknowledgement
Our work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Ministry of Science and Technology, and Beijing Natural Science Foundation.
References
- Y. Liu, et al., Nature, 2017, 543, 229-233.
- X. Yang, et al., Nature Communications, 2020, 11, 3699.
- K. Zhanghao, et al., Nature Communications, 2019, 10, 4694.
- K. Zhanghao, et al., Nature Communications, 2020, 11, 5890.
- K. Zhanghao, et al., Light: Science and Applications, 2016, 5, e16166.
Video Proceedings of Advanced Materials

Upcoming Congress



